In today’s digital world, online security is more critical than ever. Cyber threats, including data breaches, identity theft, and hacking attempts, are on the rise.
One of the most effective ways to enhance security and protect your accounts is through Two-Factor Authentication (2FA).
This article will guide you through the importance of 2FA, different types of authentication methods, how to set it up, best practices for maintaining strong security, and emerging trends in multi-factor authentication.
What is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security mechanism that requires users to provide two different authentication factors to verify their identity when logging into an online account.
Unlike traditional single-factor authentication (which relies solely on a password), 2FA enhances security by requiring an additional layer of verification.
Benefits of 2FA
- Enhanced Security: Reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Protection Against Phishing: Even if your password is compromised, attackers cannot access your account without the second factor.
- Compliance with Security Standards: Many organizations and regulations mandate 2FA to protect sensitive data.
- Increased User Confidence: Users feel safer knowing their accounts are better protected.
- Prevention of Brute Force Attacks: Even if an attacker guesses or steals your password, they still need the second factor to access your account.
- Better Access Control: 2FA allows organizations to enforce stricter security policies on critical accounts.
ALSO READ: How to Start a Blog and Make It Successful in 2025?
Types of Two-Factor Authentication

There are multiple types of 2FA methods, each with its own level of security and usability. Here are some of the most common ones:
SMS-Based Authentication
- A one-time password (OTP) is sent to the user’s registered phone number via SMS.
- Pros: Easy to set up and use.
- Cons: Susceptible to SIM swapping and interception attacks.
- Use Case: Suitable for personal accounts but not recommended for highly sensitive data.
Authentication Apps
- Apps like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, and Authy generate time-sensitive OTPs.
- Pros: More secure than SMS-based authentication.
- Cons: Requires installation and setup; losing the device may cause login issues.
- Use Case: Ideal for businesses, financial accounts, and high-security environments.
Hardware Security Keys
- YubiKey and Titan Security Key are physical devices that must be plugged into a computer or connected wirelessly.
- Pros: Extremely secure, resistant to phishing and remote attacks.
- Cons: Can be lost or damaged; some services may not support them.
- Use Case: Best for organizations and high-risk accounts needing strong security.
Biometric Authentication
- Uses fingerprint, facial recognition, or retina scans as a second factor.
- Pros: Convenient and highly secure.
- Cons: Requires compatible devices and may have privacy concerns.
- Use Case: Common for smartphones, banking apps, and corporate systems.
Email-Based Authentication
- A verification link or OTP is sent to the user’s email.
- Pros: Simple and widely supported.
- Cons: Less secure, especially if the email account is compromised.
- Use Case: Basic security for non-critical accounts.
| 2FA Method | Security Level | Convenience | Risk Factor | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMS-Based | Low | High | SIM Swap, Interception | Personal Accounts |
| Authentication Apps | High | Medium | Device Loss | Business, Finance |
| Hardware Security Keys | Very High | Low | Lost Key | Enterprise, High-Risk Accounts |
| Biometric Authentication | High | High | Privacy Concerns | Mobile, Banking Apps |
| Email-Based | Medium | High | Email Compromise | Basic Security |
ALSO READ: How to Start a Healthy Morning Routine That Sticks?
How to Set Up Two-Factor Authentication
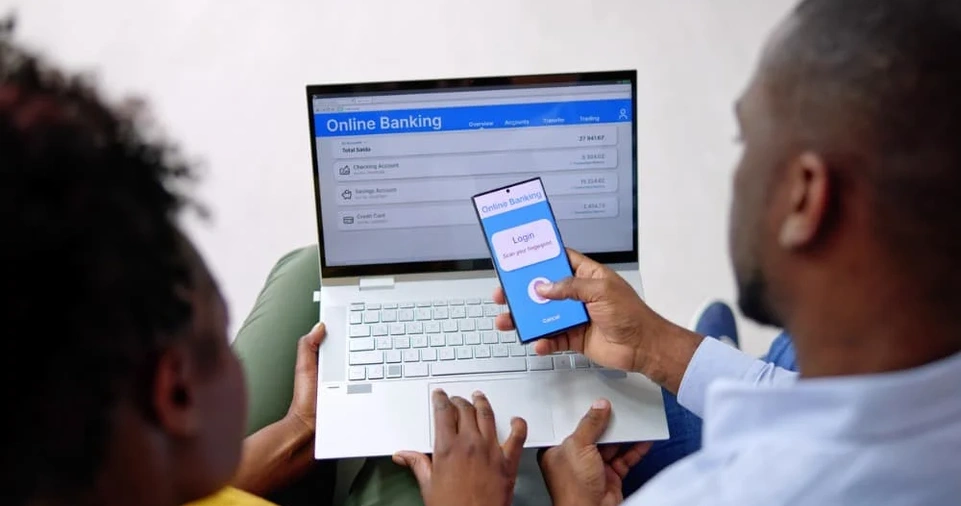
Setting up 2FA is relatively simple and varies depending on the service. Here’s a general step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Check If 2FA Is Available
- Visit the security settings of your online account (Google, Facebook, banking services, etc.).
- Look for “Two-Factor Authentication” or “Security Settings.”
Step 2: Choose Your Authentication Method
- Decide whether you want SMS, an authenticator app, a security key, or another method.
Step 3: Set Up the Authentication Method
- If using an authentication app, scan the QR code provided by the service.
- If using SMS, register your mobile number.
- If using a hardware key, follow the device’s instructions for setup.
Step 4: Save Backup Codes
- Many services provide backup codes in case you lose access to your authentication method.
- Store them in a safe place, such as a password manager.
Step 5: Test and Enable 2FA
- Complete the verification process by logging in and using the newly configured 2FA.
Best Practices for Using Two-Factor Authentication
- Avoid Using SMS 2FA If Possible: While SMS 2FA is better than no 2FA, it is vulnerable to SIM swapping and phishing attacks. Whenever possible, use an authentication app or a security key.
- Use a Password Manager: A password manager can store your passwords and 2FA backup codes securely, preventing account lockouts.
- Keep Backup Authentication Methods: Set up multiple authentication methods (e.g., an authenticator app and backup codes) to avoid being locked out.
- Update Your Recovery Information: Ensure your recovery phone number and email address are up to date in case you need to reset your 2FA settings.
- Beware of Phishing Attempts: Attackers may try to trick you into entering your 2FA codes on fake login pages. Always verify the authenticity of websites before entering your credentials.
- Regularly Review Your Security Settings: Check and update your security settings periodically to ensure all your accounts remain secure.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) uses multiple authentication factors beyond 2FA, such as combining biometrics with a hardware key for an added layer of security.
Emerging Trends in Authentication

- Passwordless Authentication: Reducing reliance on passwords through biometrics and cryptographic keys.
- AI-Powered Security: Detecting suspicious login attempts using AI-driven behavior analytics.
- Biometric Advancements: Enhancements in facial and voice recognition technologies for better security.
Conclusion
Two-Factor Authentication is an essential security measure for protecting online accounts. While it may seem inconvenient at times, the added layer of security is crucial in an era of increasing cyber threats.
By understanding the different types of 2FA and following best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and keep your personal and financial information secure.
With new advancements in authentication technology, future security measures will continue to evolve, making it even easier to protect your accounts. Start securing your accounts today by enabling 2FA on all services that support it!







